District cooling
As global temperatures continue to rise and the demand for cooling energy increases, we must seek cleaner solutions to cool our buildings and cities. District cooling is a promising option to harness free cooling from sea water and air. It can efficiently cool entire communities from a centralized chiller plant and provide free cooling to large geographical areas. By eliminating the need for individual chillers in every building, district cooling can significantly reduce environmental impact.
Why Alfa Laval in district cooling?
- Alfa Laval has been a pioneering force in plate heat exchangers for almost a century, leading the industry in innovation and sustainability.
- We recognize the growing importance of district cooling and have developed solutions specifically tailored to your needs.
- Our heat exchangers excel in district cooling, saving costs, enhancing energy efficiency, and providing superior cooling performance.
- With a global network of service centres and AHRI certification, you can count on us to provide dependable and flexible heat transfer solutions.
Trend in Industry
The cooling industry is subject to various trends. Without improving energy efficiency, space cooling energy demand is projected to more than triple by 2050, consuming a tremendous amount of electricity. Factors driving the market include growing comfort demand, population growth, decarbonization goals, effective centralized cooling systems, energy costs, and energy-efficient performance.
Some of the trends in the district cooling sector are:
- Cities are implementing more district cooling grids to meet their cooling needs sustainably.
- Rising summer temperatures in traditionally "cold countries" like the Nordics are increasing the demand for cooling.
- The shift from local chiller plants to distributed cooling grids is improving efficiency.
- Microgrids, like those surrounding shopping malls, are becoming popular starting points for larger district cooling grids.
- Global electricity scarcity is driving the adoption of free and centralized cooling in district cooling grids.

Keeping The Louvre and Mona Lisa cold
Over the years, Alfa Laval has become a true partner and has contributed, thanks to its expertise and technology, to the performance of the Climespace energy network, which is the first district cooling system in Europe and one of the biggest in the world."
Jean Levezac, Head of Cluster Connections/Substations at Climespace Engineering
The benefits of district cooling
District cooling presents a sustainable and eco-friendly solution for commercial cooling needs. By centralizing cooling services, it optimizes energy use while eliminating the need for individual electrical chillers in buildings. This not only reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions but also offers financial benefits.
With space-saving advantages and the elimination of costs associated with individual chillers, district cooling proves to be a cost-effective option. The growing global demand for this technology has prompted the industry to explore advanced heat exchanger solutions, enabling increased capacity without requiring additional infrastructure investment.

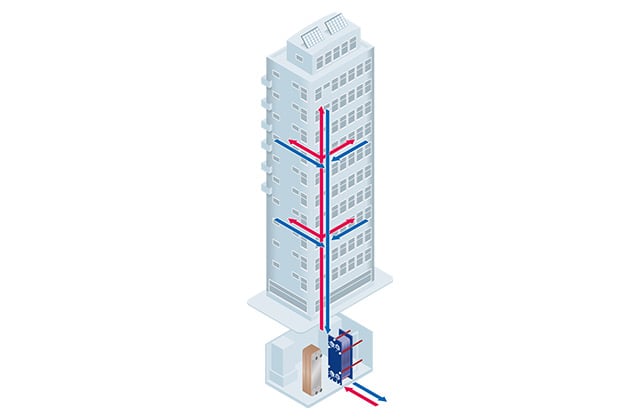
How district cooling works
District cooling efficiently distributes cooling water to buildings using heat exchanger technology from a centralized substation. The heat exchangers have two main purposes: optimizing energy usage by customizing water distribution based on specific building needs and acting as pressure-breakers to control potential damage in case of leaks.
The substation consists of a control unit, control valve, and heat exchangers. The control valve regulates water flow, while the heat exchangers modulate the temperature and capacity for each building. An energy meter measures flow rate and temperature, enabling the calculation of water consumption and final billing.
District cooling integrates energy from multiple locations, reducing stress on electricity demands, incorporating cleaner and free cooling sources, and contributing to net-zero emissions goals.
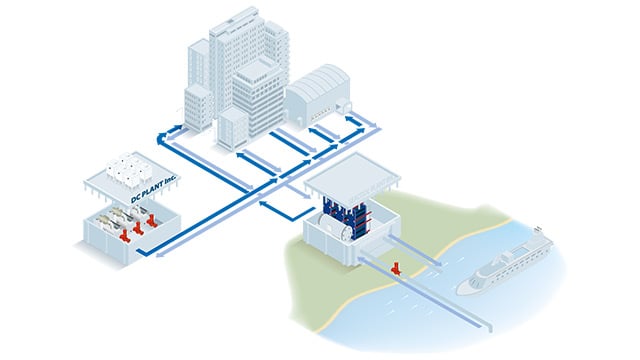
Free cooling from river or sea water
Utilizing sea and river water for free cooling significantly reduces energy consumption, with electricity only needed during extraction. This approach has a high Coefficient of Performance (COP), leading to substantial energy savings compared to traditional chillers. It also reduces the use of harmful refrigerants and fossil fuels, making it an environmentally friendly alternative.
Alfa Laval's plate heat exchanger technology is the ideal solution for safely utilizing various water sources, such as sea, brackish, river, or well water, for free cooling applications. This technology isolates the chilled water loop from sensitive equipment, eliminating the potential for corrosion, scaling, or unwarranted maintenance, ensuring reliable and consistent operation. The compact design of our plate heat exchangers offers space-saving benefits, allowing for much more efficient cooling with minimal fuss.
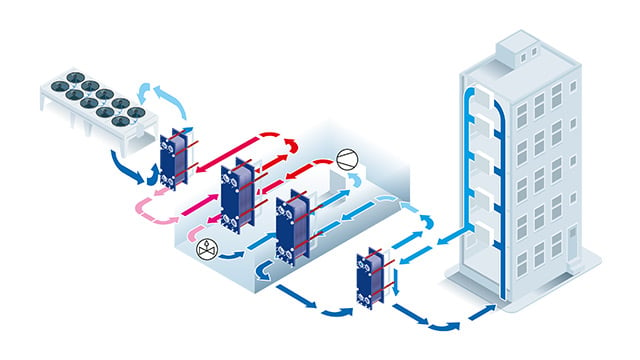
Excess heat in chiller plants can save money and decrease carbon footprint
A chiller plant's primary function is to produce cold, but it also generates excess heat as a by-product. Traditionally, this excess heat is dissipated through cooling towers and air coolers to regulate the plant's temperature. However, reusing this excess heat can be a highly beneficial solution for space heating and domestic hot water.
By recycling the excess heat generated by your chiller plant, you can reduce your reliance on fossil fuels and energy bills while decreasing your carbon footprint.
Absorption chiller – produce efficient cooling from heat
In settings where district heating and excess heat are released at elevated temperatures, a heat-driven absorption chiller can provide efficient cooling. With this approach, you can enjoy the advantages of free cooling without depending on water as your cooling source. Essentially, you can reduce both your electricity usage and the amount of conventional refrigerants required by utilizing the excess heat generated by your production processes.
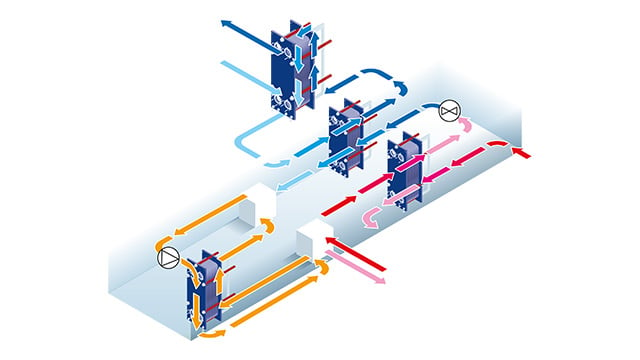
How an absorption chiller works
Within the evaporator, the refrigerant, typically water, absorbs heat from the connected system, causing the air conditioning circuit to cool via a heat exchanger. Afterward, the refrigerant enters the absorber in the form of low-pressure vapor, which is absorbed by a liquid solvent, usually lithium bromide.
A pump increases the pressure of the refrigerant, and the solvent mixture proceeds to an interchanger, where it is preheated, often using a plate heat exchanger. The resulting high-pressure vapor is then directed to the condenser, where heat is released during the refrigerant's condensation process.
Gasketed plate-and-frame heat exchangers
- Flexible solutions that can be adapted to the duty ensuring highest thermal efficiency
- Compact designs save space and are easy to service and maintain
- Solutions to reduce fouling, stress and corrosion for maximum uptime
Semi-welded plate heat exchangers
- Highly efficient, reliable technology for applications that can cause pressure or temperature fatigue
- Guaranteed long sealing lifetime thanks to unique Alfa Laval RefTight™ sealing system
- A dependable solution for preventing cross-contamination between media
Brazed plate heat exchangers
- Lightweight copper-brazed construction with compact footprint
- Greater thermal efficiency than comparable shell-and-tubes
- Flexible options to fit a variety of applications with all different types of media/fluids
- Ideal for natural and low-GWP refrigerants
Fusion bonded AlfaNova heat exchangers
- True 100% stainless steel construction
- Strong corrosion resistance with aggressive media
- Prevents metal contamination in drinking water and other hygienic applications
- High thermal efficiency and compact footprint
Consultant? System integrator?
Are you a consultant? Look here! With expertise from decades of experience in heat exchange, Alfa Laval offers knowledgeable resources for today’s heating and cooling challenges. Discover answers to complex questions on everything from energy efficiency to natural refrigerants, along with helpful tools that make it simpler to find the right technology for your application.

AHRI-performance-certified heat exchangers for confident thermal performance
Certification from the Air-Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute (AHRI) is the only global third-party verification of thermal performance, giving you independent assurance that your plate heat exchanger will perform in accordance with the manufacturer’s published ratings. Alfa Laval offers AHRI-certified gasketed plate heat exchangers, brazed plate heat exchangers, and fusion-bonded plate heat exchangers.

Making efficiency last for decades
A poorly functioning heat exchanger may affect safety, product quality and energy costs. Failure may lead to costly downtime and major losses in production. By regular and proactive maintenance of your gasketed plate heat exchanger performance is preserved and operations kept trouble-free and predictable.
We have the expertise to help you whether you experience a problem today, wish to prevent future issues or want to solve the problem yourself with our online troubleshooter.

Digitalization for energy efficiency
Smart cities and digital intelligence could help cities to make progress toward meeting 70 percent of their Sustainable Development Goals. Digital services can already have a significant impact on heating and cooling systems in cities, making them more sustainable.
Enabling remote monitoring and performing dedicated analytics allow more precise and efficient operation, more informed decision-making, and targeted interventions. The development of more sophisticated and efficient heating and cooling systems is only possible through this digital transformation, which can provide reliable and affordable heating and cooling services to urban areas while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
HVAC and the Sustainable cities
Consuming more than two-thirds of the world’s energy, our cities play a crucial role in tackling the climate crisis. A considerable part of cities’ energy consumption is for heating and cooling, which means improving energy efficiency is paramount. Alfa Laval has almost a century of experience in heat transfer and recovery and aims to become carbon neutral by 2030. Let us be your partner in the transformation to a sustainable tomorrow.









